浅谈对开发者友好的(developer-friendly)软件设计

面向开发者的软件,相比普通用户仅在限定的场景下使用外,还可能会被集成、扩展、二次开发等等,因此在代码或设计层面也应该尽可能考虑如何对开发者更友好。
本文从:
- Least Surprise
- Guide, Not Blame
- Keep It Simple, Stupid
三个不同的角度,结合实际案例,尝试阐述和讨论哪些设计是对开发者友好的。

面向开发者的软件,相比普通用户仅在限定的场景下使用外,还可能会被集成、扩展、二次开发等等,因此在代码或设计层面也应该尽可能考虑如何对开发者更友好。
本文从:
三个不同的角度,结合实际案例,尝试阐述和讨论哪些设计是对开发者友好的。

本文是对 raft paper 的翻译,原文请见 https://raft.github.io/raft.pdf
Raft 是一种用于管理 log 复制的共识算法。它采用了与 Paxos 不同的算法结构,但能产出与 (multi-)Paxos 等价的结果,并且与 Paxos 一样高效;这令 Raft 成为了比 Paxos 更易于理解且能为构建实际系统提供更好的基础的一种算法。为了更加易懂,Raft 将共识算法中的几个关键元素(比如 leader 选举,log 复制,安全等)互相分离,并通过使用更强的一致性要求来减少必须要考虑的状态(state)的数量。用户调研的结果显示 Raft 相比 Paxos 而言更容易学习。同时,Raft 还包含了一种新的通过覆盖大多数来确保安全的机制来修改集群成员。
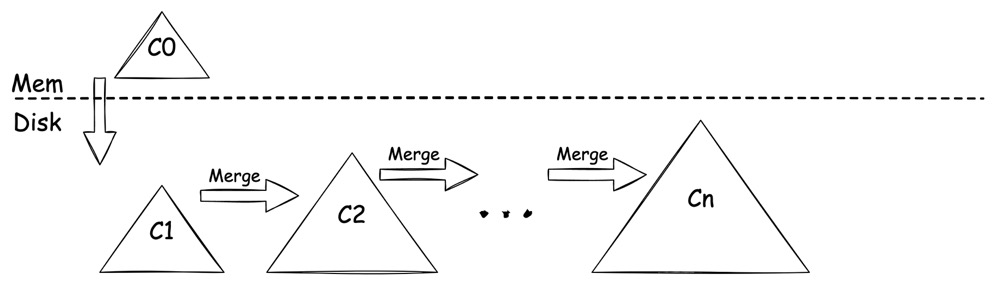
B+ Tree 与 LSM Tree 是现今各类数据库中使用的比较多的两种数据结构,它们都可以作为数据库的文件组织形式,用于以相对高效的形式来执行数据库的读写。
本文简述了这两种数据结构的操作方式与操作开销,并对比了其自身的优缺点。
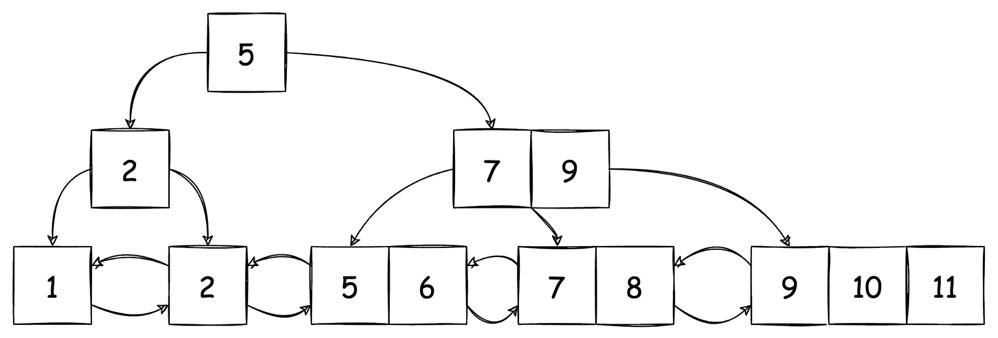
B+ Tree 与 LSM Tree 是现今各类数据库中使用的比较多的两种数据结构,它们都可以作为数据库的文件组织形式,用于以相对高效的形式来执行数据库的读写。
本文简述了这两种数据结构的操作方式与操作开销,并对比了其自身的优缺点。
Recently there's a friend ask a question in a tech group chat, he said that:
In the implementation of
CopyOnWriteArrayList.add(E e), why the writer assign the final fieldlockto a local variable ?
Then he posted a picture like this:

When I open my local JDK source and get
CopyOnWriteArrayList.add(E e), I found that the
implementation of add(E e) in my version of JDK (jdk-15)
has already refactored to just use synchronized key word
(since now the performance is better than ReentrantLock)
.
Actually the picture's version of
CopyOnWriteArrayList.add(E e) is contained in JDK 1.8, so I
switch my jdk version, and found the code, then I fell into
thought...
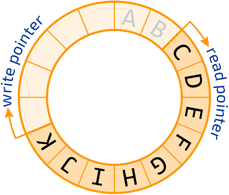
本文涉及到的代码见:https://github.com/LENSHOOD/go-lock-free-ring-buffer
Ring Buffer 是一种极其简单的数据结构,它具有如下常见的特性:
原文请见:https://martinfowler.com/articles/richardsonMaturityModel.html
最近我正在阅读一本我的几个同事一直在写的书的草稿,书名叫 Rest In Practice。他们写这本书的目的,是为了解释怎么样用 Restful web 服务来处理企业中经常面对的许多集成问题。这本书的核心概念是,web 是一种对大规模可扩展分布式系统能够工作良好的一个真实证明,并且,我们能够从中总结出一些如何更简单的构建集成系统的想法。
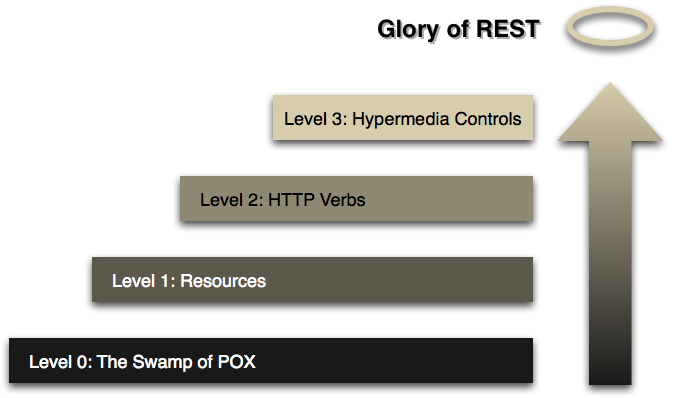
图 1:走向 REST
作者们使用了一种由 Leonard Richardson 在 QCon 大会上介绍的“restful 成熟度模型” ,来帮助解释 web-style 系统的特定属性。该模型是理解如何使用这类技术的一个好办法,因此我想尝试用自己的方式来解释它。(这里用到的协议示例仅仅用于展示,我并不觉得它值得用代码和测试来表述,因此在细节上可能存在些许问题。)
从 Java 9 开始,jdk 中提供了一个全新的类用于部分替代原本
Unsafe 所承担的偏底层的工作,即
java.lang.invoke.VarHandle。
新颖的是,在 VarHandle 中定义了对变量以不同的 Memory
Order 来进行访问的几种模式:
Plain,Opaque,Acquire/Release,Volatile
通过这几种不同的模式,在无锁编程(lock-free)中能够更灵活的控制对共享变量的操作,也能基于此更细致的进行设计从而提升程序的性能。
那么,该如何理解 VarHandle 、Memory Order、lock-free
这些概念之间的关系呢?接下来我们会从底层说起,一步步将他们串起来。
但凡提到 JUC,就一定会提到 AQS,我们能找到各种各样的文章,来分析 AQS 的实现原理,使用方法等。其原因,不仅是因为通过 AQS,JDK 衍生出了各种各样的同步工具,也因为 AQS 的优秀设计,能够使用户以非常简单的代码就能实现安全高效的同步,同时还能兼顾扩展性。
本文通过分析 AQS 的实现,来展现其优秀的设计架构与代码模型。
2020 is so special to the world. The influence of COVID-19 seems far more seriously and deeply than many people‘s estimation.
Even if the successful reaction by China government, the epidemic still cause obvious impact to every single man in this country. My salary raise frozen six months, the recruitment market seems shrink, and my company have to take many tough projects to make more money for survive.
In my feelings, time elapse so fast at 2020, one moment I were a huge musk to buy living materials, one moment it's already summer. One moment we celebrate the new year, one moment another Christmas have passed. I continue anxious about future, and continue use coding/reading to restrain it.
At the end of this year, I may say no matter it's a good year or bad year, the earth is still spinning, people we love are still getting old, and our life is still moving forward.
If use one phrase to make a conclusion, I think it will be ”basically satisfied“.